When deciding between Pharmacist vs PA, understanding the unique roles and opportunities each career offers is essential. Both paths provide rewarding experiences in the healthcare field but cater to different skill sets and interests. Whether you’re exploring the PA versus Pharmacist education journey or comparing long-term prospects like salaries and benefits, this guide will help clarify your decision.
From evaluating healthcare career comparisons to understanding the responsibilities of each role, we’ll break down key factors such as job duties, salaries, education requirements, and work environments. By the end, you’ll be equipped to choose the best career option that aligns with your goals, whether it’s becoming a pharmacist or physician assistant.
The estimated reading time is 10-12 minutes
Table of Contents

Understanding Pharmacist vs PA Roles
Core Responsibilities
Both pharmacists and physician assistants (PAs) are integral to the healthcare system, yet their responsibilities differ significantly:
Pharmacist Duties
Pharmacists specialize in the preparation, dispensing, and management of medications. They provide detailed guidance to patients about proper drug usage, monitor for potential drug interactions, and collaborate with physicians to optimize medication regimens. Their expertise lies in pharmacology and ensuring the safe administration of drugs.
PA Clinical Scope
Physician assistants have a broader clinical scope. They diagnose illnesses, develop treatment plans, and perform minor medical procedures under a supervising physician’s guidance. PAs often handle patient consultations, physical exams, and follow-ups, making them versatile contributors in medical settings.
Team Collaboration
Pharmacists and PAs are both collaborative roles but engage with different teams. Pharmacists primarily work with healthcare providers, nurses, and patients to address medication-related needs. PAs, however, are directly involved with physicians, surgeons, and broader medical teams, often acting as the first point of contact for patients.
Key Differences
Patient Interaction
Pharmacists typically engage with patients at the point of medication delivery, providing education and addressing concerns. PAs, on the other hand, have ongoing patient interactions, from initial diagnosis to follow-up care.
Decision-Making Authority
Pharmacists advise on medication use but don’t typically make diagnostic or treatment decisions. PAs, however, are empowered to make medical decisions, prescribe medications, and take a more active role in direct patient care.
Specialty Focus
Pharmacists focus on medication therapy management and optimizing pharmacological care. In contrast, PAs can specialize in various medical fields such as cardiology, orthopedics, or dermatology, offering diverse career trajectories.
Understanding these distinctions is essential when deciding between pursuing a career as a pharmacist or a PA, as each role caters to unique skills, interests, and professional goals.
Education Path: Pharmacist vs PA Requirements

Academic Journey
Undergraduate Prerequisites
Both pharmacists and physician assistants (PAs) begin their career paths with a strong foundation in science. Aspiring pharmacists typically pursue pre-pharmacy courses, focusing on subjects like biology, chemistry, and mathematics. For PAs, undergraduate programs emphasize anatomy, physiology, and health sciences, often supplemented by patient care experience.
Graduate Program Length
Pharmacists enter a Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) program, which usually takes 4 years to complete. This program blends classroom education with practical training in pharmacology, patient care, and pharmacy management.
PAs, on the other hand, enroll in a Master’s in Physician Assistant Studies or similar programs, which typically span 2–3 years. PA education combines didactic coursework in medical sciences with clinical rotations across multiple specialties.
Clinical Rotations
Clinical experience varies significantly between the two roles. Pharmacists complete rotations in pharmacy settings, focusing on medication therapy and patient counseling. PAs undergo more extensive clinical rotations in diverse medical fields, such as family medicine, surgery, and pediatrics, preparing them for direct patient care roles.
Certification Process
State Licensing
Both careers require state licensure. Pharmacists must pass the North American Pharmacist Licensure Examination (NAPLEX) and, in some cases, a state-specific law exam. PAs must clear the Physician Assistant National Certifying Exam (PANCE) to practice.
Board Examinations
While board certification is optional for pharmacists, it enhances career prospects in specialized fields like oncology or geriatrics. For PAs, board certification through the National Commission on Certification of Physician Assistants (NCCPA) is essential to maintain their credentials.
Continuing Education
Both pharmacists and PAs must engage in lifelong learning to retain their licenses. Pharmacists complete continuing education units (CEUs) focused on new drug therapies and regulations, while PAs fulfill ongoing certification requirements through periodic exams and medical training.
Choosing between a career as a pharmacist or a PA often depends on the desired educational commitment and professional focus, with each path offering unique opportunities for growth and specialization.
Pharmacist vs PA: Salary & Benefits Comparison
Financial Overview
Starting Salaries
When comparing entry-level salaries, physician assistants (PAs) generally have a slight edge. PAs earn an average starting salary of $95,000–$105,000 annually, thanks to their clinical responsibilities and patient care focus. Pharmacists, by contrast, typically start at $85,000–$100,000, depending on their location and practice setting.
Mid-Career Earnings
Mid-career professionals see a significant increase in their earnings. Pharmacists can earn $120,000–$130,000, particularly in retail or hospital settings. PAs, especially those specializing in areas like surgery or emergency medicine, report similar earnings of $115,000–$130,000.
Senior-Level Income
At senior levels, both professions offer lucrative compensation. Pharmacists with extensive experience or management roles can earn up to $140,000+, especially in specialized fields like oncology or clinical research. PAs in leadership positions or high-demand specialties may also earn $135,000–$150,000 annually.

Benefits Analysis
Healthcare Coverage
Both pharmacists and PAs enjoy comprehensive healthcare benefits. These often include medical, dental, and vision coverage, with many employers offering competitive packages. PAs may sometimes receive additional perks like malpractice insurance, reflecting their direct patient care roles.
Retirement Options
Both roles benefit from strong retirement savings options, such as 401(k) plans with employer contributions. Pharmacists in large hospital systems or corporate settings often have access to enhanced retirement plans, while PAs may receive additional bonuses tied to their performance or practice profitability.
Professional Perks
Pharmacists often receive perks such as flexible scheduling, tuition reimbursement, and employee discounts on healthcare products. PAs benefit from professional liability insurance, continuing education allowances, and opportunities for career advancement through employer-funded certifications or training programs.
In summary, while both pharmacists and PAs enjoy high earning potential and robust benefits, specific financial rewards and perks may vary based on individual roles, work settings, and career stages.
Work Environment: PA vs Pharmacist
Practice Settings
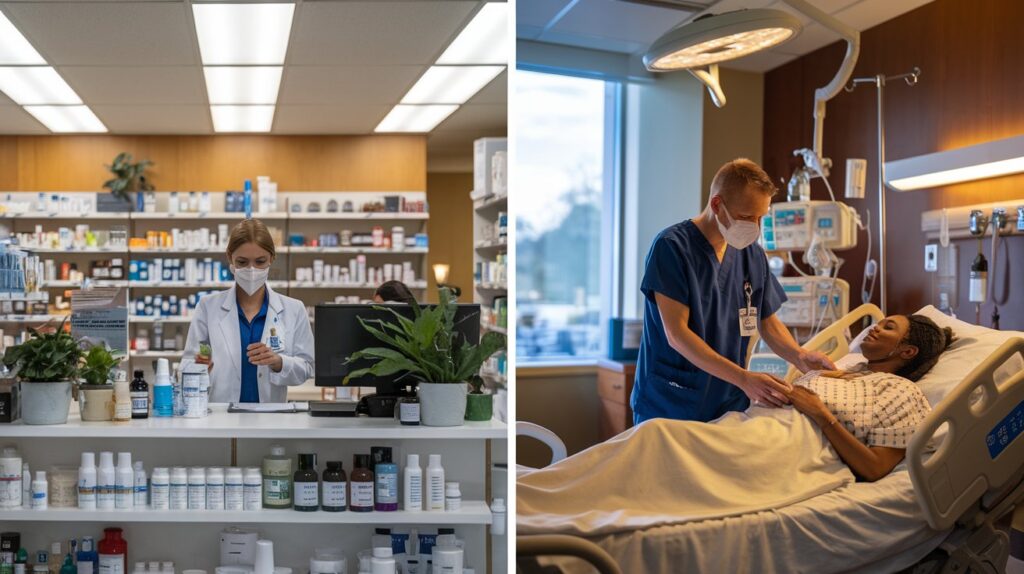
Hospital Environment
Physician assistants often work directly within hospital teams, contributing to patient care plans, assisting in surgeries, and responding to medical emergencies. Pharmacists in hospital settings play a crucial role in managing medications, ensuring that treatments align with patient needs, and collaborating with other healthcare professionals. Comparing these career paths, it’s evident that the Pharmacist vs PA roles are distinct yet complementary in hospital environments.
Clinical Settings
PAs frequently operate in outpatient clinics, delivering diagnostic and therapeutic services under a physician’s supervision. On the other hand, pharmacists in clinical settings provide consultations to patients, monitor chronic conditions, and optimize medication regimens. This difference in focus highlights the diversity in responsibilities when evaluating a career in healthcare job comparison.
Private Practice
PAs working in private practices often enjoy a mix of autonomy and direct patient care, particularly in underserved areas. Pharmacists in private practice focus more on dispensing medications, managing inventory, and providing personalized healthcare advice. For those exploring medical career paths, private practice offers unique opportunities tailored to each profession’s strengths.
Schedule Comparison
Work Hours
PAs generally work 40–60 hours per week, with schedules that vary depending on their specialty. For instance, emergency medicine or surgical PAs may work extended shifts, while those in outpatient settings often maintain more regular hours. Pharmacists typically have a schedule ranging from 30–50 hours per week, with retail roles often requiring evening or weekend work. Comparing PA vs Pharmacist salary, work hours can influence earning potential significantly.
On-Call Duties
On-call responsibilities are more common for PAs, especially those in surgical or emergency care. Pharmacists, while rarely on-call, may need to be available during emergencies in hospital settings or to review critical medication orders. This aspect of healthcare career comparison is an important consideration for those deciding between the two paths.
Shift Flexibility
While PAs might face unpredictable schedules, especially in high-demand specialties, pharmacists generally enjoy greater stability. Retail pharmacists, for example, often have defined shifts, which makes the career appealing to those valuing work-life balance. For individuals evaluating Pharmacist or PA career choice, schedule flexibility can be a deciding factor.
By examining the work environments of PAs and pharmacists, prospective professionals can align their career goals with the settings and schedules that best suit their personal and professional aspirations.
Career Growth: Pharmacist vs PA Opportunities
Advancement Paths
Specialization Options
For physician assistants, specialization in fields like cardiology, orthopedics, or dermatology can significantly enhance career prospects and earning potential. Pharmacists also have diverse specialization opportunities, including clinical pharmacy, oncology, and pharmacogenomics. These specialization options are critical for anyone comparing Pharmacist vs PA career paths, as they allow professionals to focus on areas of personal interest while advancing their careers.
Leadership Roles
PAs often transition into leadership roles such as clinical directors or department heads, leveraging their medical expertise and teamwork capabilities. Pharmacists can also ascend to leadership positions, such as pharmacy managers or directors of pharmacy operations, overseeing large teams and complex systems. Evaluating leadership growth is essential when considering healthcare job comparison for long-term career planning.
Research Opportunities
Both careers offer opportunities to contribute to healthcare innovation. PAs may participate in clinical trials or assist physicians in medical research, while pharmacists often engage in pharmaceutical research, drug development, or academic studies. This focus on research underscores the importance of career growth potential in clinical career options for both professions.
Future Outlook
Industry Trends
The growing demand for healthcare professionals ensures a positive outlook for both pharmacists and PAs. Emerging trends, such as telemedicine and personalized medicine, are reshaping how care is delivered, creating new opportunities for these roles. Understanding these trends is vital for those comparing medical professional roles in a dynamic industry.
Job Market Projections
The job market for PAs is expected to grow by 27% through 2031, driven by the increasing demand for healthcare services in underserved areas. Pharmacists, while facing a more competitive retail market, are seeing growth in clinical and specialized roles. Considering PA versus Pharmacist education and market projections can help professionals choose a stable and rewarding career.
Emerging Roles
For PAs, new roles in remote patient monitoring and preventive care are opening up, reflecting the shift toward holistic healthcare. Pharmacists are also finding opportunities in areas like pharmacovigilance, digital health, and sustainability initiatives within the pharmaceutical industry. These emerging roles demonstrate the evolving landscape of Pharmacist or PA career choice in 2024.
Whether through specialization, leadership, or adapting to future trends, both pharmacists and PAs have robust career growth opportunities that make them excellent options for aspiring healthcare professionals.
Making the Choice: PA or Pharmacist?
Decision Factors
Personal Interests
Choosing between Pharmacist vs PA careers often begins with assessing personal interests. If you are passionate about medication management, drug therapies, and working behind the scenes in healthcare, becoming a pharmacist might be the right path. On the other hand, if you enjoy direct patient interaction, diagnosing illnesses, and working closely with physicians, the PA profession might align better with your interests.
Skills Assessment
Evaluate your skills when deciding between healthcare career comparison options. Pharmacists excel in analytical thinking, attention to detail, and a deep understanding of pharmacology. PAs, however, thrive with strong communication, diagnostic, and hands-on clinical skills. Comparing these skill sets can clarify which career suits your strengths.
Lifestyle Preferences
Lifestyle considerations play a significant role in choosing between these professions. PAs often have unpredictable schedules, including on-call duties, but benefit from varied and dynamic work environments. Pharmacists typically have more predictable hours, especially in retail or hospital settings, but may face repetitive tasks. Weighing these lifestyle preferences is essential for selecting the best Pharmacist or PA career choice.
Career Planning
Short-Term Goals
Establishing short-term goals can guide your decision. For aspiring PAs, completing clinical rotations and obtaining state licensure are immediate steps toward starting a practice. For pharmacists, earning a Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.) degree and passing board exams are key initial milestones. Focusing on these short-term goals ensures a smooth start in your chosen career path.
Long-Term Objectives
Long-term objectives are equally important in a medical career paths decision. Pharmacists might aim to specialize in fields like oncology or pharmacogenomics, while PAs could aspire to lead a clinical department or work in high-demand specialties like cardiology. Defining your ultimate career aspirations will help determine the most suitable path.
Investment Considerations
Financial and time investment is a critical factor when choosing between PA versus Pharmacist education. A PA career typically requires fewer years of education, though clinical training can be intense. Pharmacists often spend more years in school and may graduate with higher student debt but benefit from consistent earning potential. Understanding these investment considerations ensures a well-informed career choice.
Whether you prioritize personal interests, skills alignment, or long-term goals, deciding between a career as a pharmacist or PA involves careful thought and planning. Both roles offer unique opportunities for growth and fulfillment in the healthcare industry.
Expert Insights: Pharmacist vs PA Career Paths
Professional Perspectives
Current Practitioners
Insights from current practitioners shed light on the real-world aspects of Pharmacist vs PA careers. Pharmacists often emphasize the importance of staying updated with the latest advancements in drug therapies and the satisfaction of ensuring patient safety through accurate medication management. PAs highlight the fulfillment of diagnosing illnesses, developing treatment plans, and witnessing direct improvements in patient health.
Healthcare Managers
Healthcare managers provide a broader perspective on these roles. They value pharmacists for their expertise in managing medication inventory, supporting interdisciplinary teams, and contributing to patient care quality. On the other hand, PAs are seen as adaptable team players who bridge the gap between physicians and patients, offering critical support in high-pressure clinical settings.
Career Advisors
Career advisors stress aligning your career choice with your personality and professional goals. For those who enjoy structured, methodical work with a strong emphasis on science, pharmacy is an excellent fit. For individuals drawn to fast-paced environments with diverse patient interactions, becoming a PA offers unique opportunities. These advisors often recommend shadowing professionals in both fields to gain first-hand experience.
Success Stories
Career Transitions
Many professionals successfully transition between related medical career paths, demonstrating that initial choices need not be final. For example, a pharmacist might pivot into a consulting role, advising healthcare organizations on medication safety. Similarly, a PA might advance into healthcare leadership, managing clinical operations or leading a team of medical professionals.
Achievement Milestones
Achievement milestones are abundant in both careers. Pharmacists often celebrate developing innovative compounding techniques or introducing process improvements in medication management. PAs may take pride in performing life-saving procedures or becoming trusted experts in their chosen specialty.
Professional Tips
Successful professionals in both careers emphasize the importance of continuous learning. Pharmacists recommend pursuing certifications in niche areas like oncology or pharmacogenomics to boost career prospects. PAs advocate for specializing in high-demand areas like emergency medicine or orthopedics for increased job satisfaction and career advancement.
Expert insights confirm that both roles offer rewarding career opportunities, each with its unique challenges and advantages. Deciding between Pharmacist or PA career choice requires understanding your strengths and professional aspirations, with a willingness to adapt and grow in your chosen path.
FAQ: Choosing Between Pharmacist and PA
Common Questions
Educational Requirements
What are the educational requirements for pharmacists and PAs?
To become a pharmacist, you need a Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) degree, which typically takes four years after completing undergraduate prerequisites. For a PA, a Master of Science in Physician Assistant Studies or a similar program is required, which takes about two years after a bachelor’s degree. Both careers demand rigorous clinical training and state licensing.
Career Satisfaction
Which career offers more satisfaction: Pharmacist or PA?
Career satisfaction largely depends on personal interests. Pharmacists often find fulfillment in ensuring medication safety and patient education, while PAs enjoy diagnosing conditions, providing hands-on care, and directly impacting patient outcomes. Evaluating your passion for clinical interaction versus technical expertise can guide your choice.
Work-Life Balance
How do work-life balances compare in these careers?
Pharmacists often enjoy predictable schedules, particularly in retail or hospital pharmacy settings. PAs may face more demanding schedules, including on-call duties and irregular hours, depending on their specialization. However, both careers can offer flexibility with the right job choice.
Decision Support
Comparison Checklist
To help make your choice, consider the following factors:
- Education and Training Time: Do you prefer a shorter or longer academic journey?
- Patient Interaction: Are you more inclined toward direct care or behind-the-scenes support?
- Salary Expectations: What is your financial goal?
- Work Environment: Do you thrive in high-pressure clinical settings or structured environments like pharmacies?
Resource Guide
Here are helpful resources to explore:
- Shadowing Programs: Spend a day with a pharmacist or PA to see their daily responsibilities.
- Professional Organizations: Visit websites like the American Pharmacists Association (APhA) and the American Academy of PAs (AAPA).
- Career Counseling Services: Seek advice from career advisors experienced in healthcare career comparison.
Next Steps
- Reflect on your personal interests and professional goals.
- Research accredited PharmD or PA programs and their admission criteria.
- Gain practical experience through internships or volunteering in relevant healthcare settings.
Choosing between a pharmacist or PA career is a significant decision, but with careful evaluation of your priorities and strengths, you can select a path that aligns with your aspirations.

Conclusion
Choosing between a career as a pharmacist or a physician assistant is a significant decision, as both roles offer unique rewards, challenges, and growth opportunities. Pharmacists excel in providing specialized knowledge about medications and their applications, while PAs thrive in hands-on patient care and medical decision-making.
When deciding which career path to pursue, consider your interests, skills, and long-term goals. Whether you’re drawn to the structured expertise of pharmacy or the dynamic, patient-centered approach of a PA, both careers provide fulfilling ways to make a meaningful impact in healthcare.
Ultimately, the choice comes down to aligning your passions with the career that best fits your personal and professional aspirations. With the insights provided in this guide, you’re better equipped to evaluate the opportunities and challenges of each role and take the first step toward a rewarding future.
References
- American Pharmacists Association (APhA). Pharmacy Career Pathways. apha.org
- National Commission on Certification of Physician Assistants (NCCPA). Physician Assistant Career Resources. nccpa.net
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Occupational Outlook Handbook: Pharmacists. bls.gov
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Occupational Outlook Handbook: Physician Assistants. bls.gov
- The Balance Careers. Pharmacist vs. Physician Assistant Career Comparison. thebalancecareers.com




